XiaNaphryz
LATIN, MATRIPEDICABUS, DO YOU SPEAK IT
http://www.sfgate.com/cgi-bin/article.cgi?f=/n/a/2011/04/01/state/n205845D63.DTL&ao=all



The main concern with skin issues is that it may cause explosive decompression and then something like Aloha Airlines Flight 243 may be repeated which was also a Boeing 737, albeit an older design:

(04-02) 12:21 PDT PHOENIX, AZ (AP) -- Flight attendants had begun to take drink orders when the explosion rocked the cabin.
Aboard Southwest Flight 812, Shawna Malvini Redden covered her ears, then felt a brisk wind rush by. Oxygen masks fell, the cabin lost pressure and Redden, now suddenly lightheaded, fumbled to maneuver the mask in place.
Then she prayed. And, instinctively, reached out to the stranger seated next to her in Row 8 as the pilot of the damaged aircraft began a rapid descent from some 34,400 feet in the sky.
"I don't know this dude but I was like, 'I'm going to just hold your hand,'" Redden, a 28-year-old doctoral student at Arizona State University, recalled Saturday, a day after her Phoenix-to-Sacramento flight was forced into an emergency landing at a military base in Yuma, Ariz., with a gaping hole in its fuselage.
No serious injuries were reported among the 118 people aboard , according to Southwest officials.
What caused the part of the fuselage to rupture on the 15-year-old Boeing 737-300 was a mystery, and investigators from the National Transportation Safety Board arrived in Yuma on Saturday morning to begin an inquiry.
Southwest, meanwhile, grounded about 80 similar planes in its fleet for inspections, and said that some 300 flights likely would be canceled Saturday because of the reduced fleet.
Southwest operates about 170 of the 737-300s in its fleet of about 540 planes, but it replaced the aluminum skin on many of the 300s in recent years, spokeswoman Linda Rutherford said. The planes that were grounded Saturday have not had their skin replaced, she said.
"Obviously we're dealing with a skin issue, and we believe that these 80 airplanes are covered by a set of (federal safety rules) that make them candidates to do this additional inspection that Boeing is devising for us," Rutherford said.
Julie O'Donnell, an aviation safety spokeswoman for Seattle-based Boeing Commercial Airplanes, confirmed "a hole in the fuselage and a depressurization event" in the latest incident but declined to speculate on what caused it.
There are a total of 288 Boeing 737-300s currently operating in the U.S. fleet, and 931 operate worldwide, according to the Federal Aviation Administration. "The FAA is working closely with the NTSB, Southwest Airlines and Boeing to determine what actions may be necessary," the FAA said in a statement released Saturday.
Southwest officials said the Arizona plane had undergone all inspections required by the FAA. They said the plane was given a routine inspection on Tuesday and underwent its last so-called heavy check, a more costly and extensive overhaul, in March 2010.
The 737-300 is the oldest plane in Southwest's fleet, and the company is retiring 300s as it take deliveries of new Boeing 737-700s and, beginning next year, 737-800s. But the process of replacing all the 300s could take years.
Seated one row from the rupture, Don Nelson said it took about four noisy minutes for the plane to dip to less than 10,000 feet. "You could tell there was an oxygen deficiency," he said.
"People were dropping," said Christine Ziegler, a 44-year-old project manager from Sacramento who watched as the crew member and a passenger nearby fainted. Nelson and Ziegler spoke after a substitute flight took them on to Sacramento.
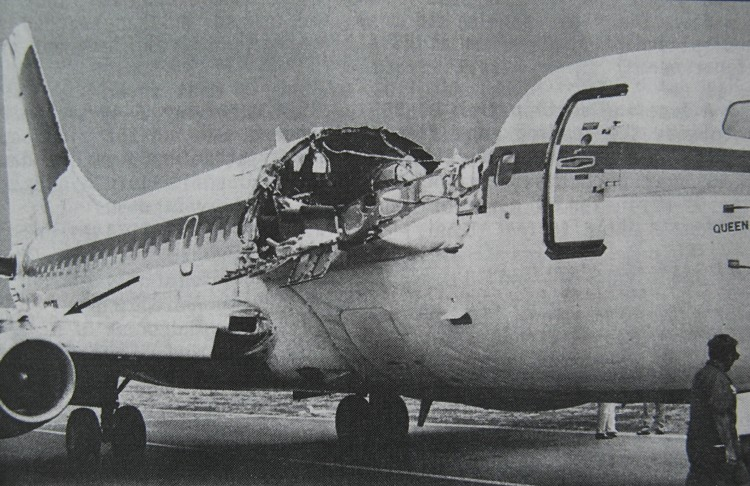
Brenda Reese described the hole as "at the top of the plane, right up above where you store your luggage."
"The panel's not completely off," she told The Associated Press. "It's like ripped down, but you can see completely outside... When you look up through the panel, you can see the sky."
Cellphone photographs provided by Reese showed a panel hanging open in a section above the plane's middle aisle.
At an altitude of over 34,000 feet, the Southwest pilots would have had only 10 to 20 seconds of "useful consciousness" to get their oxygen masks on or pass out, said John Gadzinski, an airline pilot and aviation safety consultant.
"The higher you are the less useful consciousness time you have," said Gadzinski, president of Four Winds Consulting in Virginia Beach, Va. "It's a credit to the pilots that they responded so quickly."
A loss of cabin pressure just after takeoff knocked out the pilots of a Helios Airways Boeing 737 in August 2005. The plane flew into a hillside north of Athens in Greece, killing all 121 people aboard. In that case, an investigation found the pilots had failed to heed a warning that the pressurization system wasn't working correctly.
In this case, the hole and subsequent depressurization wouldn't have affected the pilots' ability to control the plane as long as they had their oxygen masks on, Gadzinski said.
"The fact that you have a breach hole doesn't affect the aerodynamics of the plane. The plane still flies exactly the same," he said.
A similar incident happened in July 2009 when a football-sized hole opened up in flight in the fuselage of another Southwest 737, depressurizing the cabin. The plane made an emergency landing in Charleston, W.Va. It was later determined that the hole was caused by metal fatigue.
Afterward, Southwest and the FAA reached an agreement specifying actions the airline would take to prevent another episode, said John Goglia, a former National Transportation Safety Board member and an expert on airline maintenance. The details of that agreement are considered proprietary and haven't been made public, he said.
The latest incident "certainly makes me think there is something wrong with the maintenance system at Southwest and it makes me think there is something wrong with the (FAA) principal maintenance inspector down there that after that big event they weren't watching this more closely," Goglia said in an interview.
There was "never any danger that the plane would fall out of the sky," Goglia said. "However, anybody on that airplane with any sort of respiratory problems certainly was at risk."
Four months before that emergency landing, the Dallas-based airline had agreed to pay $7.5 million to settle charges that it operated planes that had missed required safety inspections for cracks in the fuselage. The airline, which flies Boeing 737s, inspected nearly 200 of its planes back then, found no cracks and put them back in the sky.
In 1988, cracks caused part of the roof of an Aloha Airlines Boeing 737 to peel open while the jet flew from Hilo to Honolulu. A flight attendant was sucked out of the plane and plunged to her death, and dozens of passengers were injured.
Three years ago, an exploding oxygen cylinder ripped a gaping hole the fuselage of a Qantas Boeing 747-438 carrying 365 people. The plane descended thousands of feet with the loss of cabin pressure and flew about 300 miles to Manila, where it made a successful emergency landing. No one was injured.
As for Friday's flight, there was obvious relief when it touched down safely. And when the pilot emerged after the landing, the atmosphere turned celebratory, Redden said.
"When the pilot came out a little bit later to look at the damage, we clapped and cheered. If overhead bins weren't in the way, I'm pretty sure we would've given him a standing ovation," she said.



The main concern with skin issues is that it may cause explosive decompression and then something like Aloha Airlines Flight 243 may be repeated which was also a Boeing 737, albeit an older design:
Around 13:48, as the aircraft reached its normal flight altitude of 24,000 feet (7,300 m) about 23 nautical miles (43 km) south-southeast of Kahului, a small section on the left side of the roof ruptured. The resulting explosive decompression tore off a large section of the roof, consisting of the entire top half of the aircraft skin extending from just behind the cockpit to the fore-wing area.[2]
As part of the design of the 737, stress may be alleviated by controlled area breakaway zones. The intent was to provide controlled depressurization that would maintain the integrity of the fuselage structure. The age of the plane and the condition of the fuselage (that had corroded and was stressing the rivets beyond their designed capacity) appear to have conspired to render the design a part of the problem; when that first controlled area broke away, according to the small rupture theory, the rapid sequence of events resulted in the failure sequence. This has been referred to as a zipper effect.
First Officer Madeline "Mimi" Tompkins' head was jerked back during the decompression, and she saw cabin insulation flying around the cockpit. Captain Robert Schornstheimer looked back and saw blue sky where the first class cabin's roof had been. Tompkins immediately contacted Air Traffic Control on Maui to declare mayday, switching duties with Captain Schornstheimer, who from this point on, took over control of the plane, as it is usually customary for the Captain to take over a flight that enters a state of emergency.
At the time of the decompression, the chief flight attendant, Clarabelle "C.B." Lansing, was standing at seat row 5 collecting drink cups from passengers. According to passengers' accounts, Lansing was blown out through a hole in the side of the airplane by the greater air pressure remaining in the cabin.





