entremet
Member
It wasn't phases of homo sapiens but just one huge wave.
Pretty interesting finding for our species's natural history.
Also, we leave Africa? Climate models show it may have been a rainfall issue, which affected available food and thus our ancestors went looking for food.
Food, making the world go around since the dawn of humanity.
Full article: http://www.nytimes.com/2016/09/22/science/ancient-dna-human-history.html?_r=0
Pretty interesting finding for our species's natural history.
Also, we leave Africa? Climate models show it may have been a rainfall issue, which affected available food and thus our ancestors went looking for food.
Food, making the world go around since the dawn of humanity.
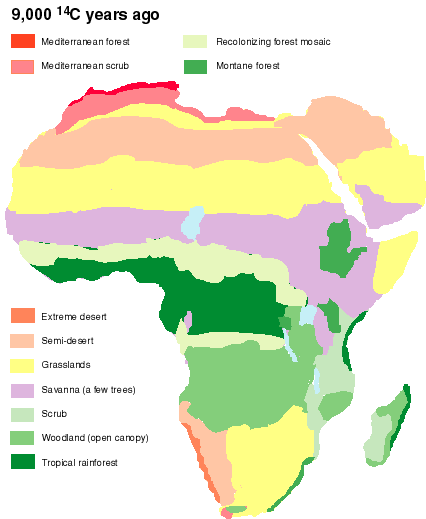
Modern humans evolved in Africa roughly 200,000 years ago. But how did our species go on to populate the rest of the globe?
The question, one of the biggest in studies of human evolution, has intrigued scientists for decades. In a series of extraordinary genetic analyses published on Wednesday, researchers believe they have found an answer.
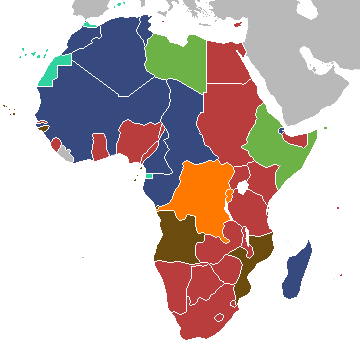
In the journal Nature, three separate teams of geneticists survey DNA collected from cultures around the globe, many for the first time, and conclude that all non-Africans today trace their ancestry to a single population emerging from Africa between 50,000 and 80,000 years ago.
“I think all three studies are basically saying the same thing,” said Joshua M. Akey of the University of Washington, who wrote a commentary accompanying the new work. “We know there were multiple dispersals out of Africa, but we can trace our ancestry back to a single one.”
Early studies of bits of DNA also supported this idea. All non-Africans are closely related to one another, geneticists found, and they all branch from a family tree rooted in Africa.
Yet there are also clues that at least some modern humans may have departed Africa well before 50,000 years ago, perhaps part of an earlier wave of migration.
In Israel, for example, researchers found a few distinctively modern human skeletons that are between 120,000 and 90,000 years old. In Saudi Arabia and India, sophisticated tools date back as far as 100,000 years.
Last October, Chinese scientists reported finding teeth belonging to Homo sapiens that are at least 80,000 years old and perhaps as old as 120,000 years.
Full article: http://www.nytimes.com/2016/09/22/science/ancient-dna-human-history.html?_r=0